Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic condition that significantly affects patients’ quality of life. Managing IBS is complex, involving both physical and psychological symptoms that can be difficult to control. Digital health interventions (DHIs) have the potential to empower patients with self-management tools, however, research on their effectiveness in IBS treatment is limited, and there is a lack of evidence on their feasibility and long-term use. The need for equitable and inclusive access to IBS care, particularly for underserved IBS populations, highlights the urgency for innovative solutions, particularly in digital health interventions (DHIs), can address this unmet need and empower patients with self-management tools.
IMAGINE partnered with the Health System Impact Fellowship to co-sponsor post-doc fellow, Dr. Adrijana d’Silva, to conduct a systematic review of existing self-directed care and patient empowerment IBS digital tools that improve health outcomes through education, diet management, brain-gut behavior skills, health monitoring, and community support. This work was published recently in Digestive Disease and Sciences. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-024-08672-7) D’Silva received comprehensive training and mentorship in health systems research (methodologies, impact evaluation, and policy translation through HSIF’s National Cohort Training Program (NCTP). By identifying the types of DHIs that offer the most significant improvements, our findings provide a roadmap for expanding these interventions to more patients across community health centers, hospitals, and digital platforms.
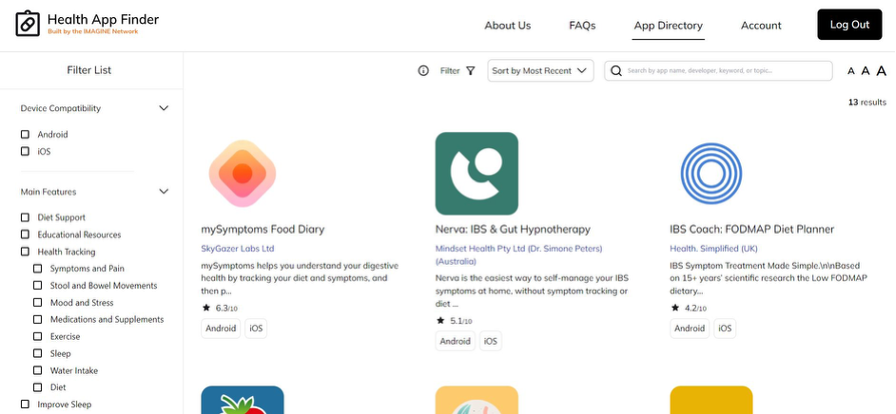
This preliminary research served as the foundation for the One-Stop-Shop (OSS) for IBS platform (recently renamed “Health App Finder”). This IMAGINE-funded project, led by d’Silva, aims to develop an online platform designed to help IBS patients find, filter, and review various IBS-related apps aimed at managing their condition. It serves as a comprehensive database of apps, with options to search by app type, cost, user ratings, and features like diet tracking or symptom monitoring. Users can leave star ratings and detailed reviews, sharing personal experiences about effectiveness, ease of use, and technical reliability. This platform empowers IBS patients by giving them the ability to make informed decisions based on community feedback and expert recommendations, ensuring they find apps that truly meet their needs. This work was made possible through collaboration among a multidisciplinary team of researchers, patient partners, healthcare professionals, technology developers, and patient advocacy groups. Our patient partners provided insights into how IBS patients can better manage their condition with digital tools. To sustain the portal in the long-term, IMAGINE is partnering with the Gastrointestinal Society to host the portal on their website. Thanks to this partnership, IBS patients will have greater access to self-management resources. Furthermore, the Gastrointestinal Society envisions expanding the scope of the portal to support patients with other GI disorders.
OSS presents a novel, scalable option to improve IBS care. The impact of this work is far-reaching, touching patients directly as well as the potential to influence healthcare providers and policymakers who are seeking innovative, scalable solutions for IBS management. Our work also emphasizes the importance of patient engagement in the development and evaluation of these interventions to ensure they meet the needs of diverse IBS populations. This work has added depth to understanding how to improve health system efficiency and patient outcomes via self-management.
In a related initiative, our Implementation Science Lead, Dr. Justin Presseau, is leading working group investigating how to support the uptake and sustained use of digital solutions/apps in IBD/IBS care. The goal of this group is to develop a framework of evidence-informed strategies to support the sustained use of digital health tools. IMAGINE 2.0 Network has established a working group to lead initiatives that support the widespread and sustained use of digital health tools for IBD and IBS care. This group includes people living with IBD and IBS, healthcare providers, researchers, and representatives from IMAGINE’s partner organizations, all focused on maximizing the benefits of digital health for IBD and IBS. A key focus of the group is helping people with IBD and IBS to keep using these tools over time, as ongoing use is sometimes needed to get the benefit of these tools. However, many people stop using tools like self-management apps and medication trackers, limiting their potential benefits. To address this, we are interviewing people with IBD and IBS to understand their experiences and identify barriers to ongoing use. So far, 14 people have been interviewed, with plans to speak with about 16 more. Insights from these interviews will guide the identification of evidence-based strategies, known as behaviour change techniques, to encourage sustained use. By working with patient partners to tailor these strategies, the group aims to empower people with IBD and IBS to make the most of digital health tools, ultimately improving their quality of life and healthcare experience. These strategies will be widely shared with people with IBD and IBS and with researchers and tool developers, helping to shape future digital tools that better meet users’ needs. A manuscript entitled, “Health Care Practitioner Perceptions of Barriers and Enablers to Implementing Digital Health Technologies for Chronic Condition Self-Management in Primary Care Settings: A Scoping Review Protocol” has already been submitted and approved for publication by BMJ Open.
Another focus is promoting the use of digital health tools in primary care settings, where providers can play a critical role in recommending these tools to patients. Primary care providers are in an ideal position to encourage patients to use digital tools to manage conditions like IBD and IBS, but various barriers can prevent this. To identify these challenges, some members of the working group are conducting a scoping review of studies where healthcare providers have shared their views on recommending digital health tools. This information will be summarized and used to identify and tailor strategies that could help primary care providers more easily integrate these recommendations into their practice. With the support of IMAGINE’s members across Canada, these strategies will be shared with healthcare providers, researchers, and advocates, helping to create a healthcare environment where digital health tools become a standard part of managing IBD and IBS.
Our work on Digital Health Tools has fostered stronger relationships between researchers and the patient community. It has been an exemplar on how to bridge the gap between research and practical, real-world applications. By addressing barriers to both patient and provider use of digital health tools, the working group’s efforts have the potential to drive meaningful improvements in IBD and IBS care. Their work will enable more people to access and benefit from these tools, fostering better self-management and ultimately leading to better health outcomes across Canada.
